Bromhexine HCL
2200.0 INR/Number
Product Details:
- Molecular Formula C14H20Br2N2 HCl
- Taste Bitter
- Loss on Drying not more than 1% by weigh
- Melting Point ~ 165-167 C (329-333 F)
- Boiling point 441.5 AdegC at 760 mmHg
- Heavy Metal (%) not exceed 20 ppm
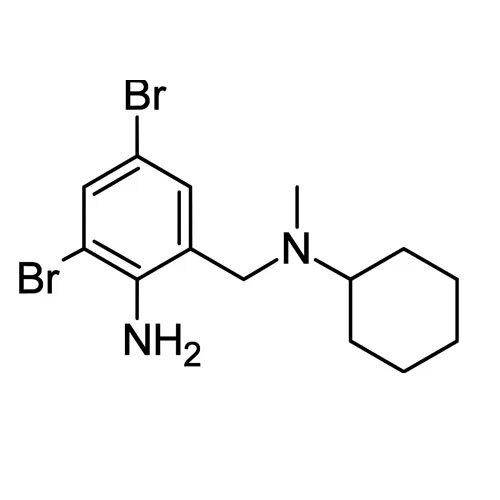
- Structural Formula Br | H2N-C6H12-CH2-C6H12-CH2-NH2 | Br
- Click to View more
X
Bromhexine HCL Price And Quantity
- 2200.0 INR/Number
- 25 Number
Bromhexine HCL Product Specifications
- 2 Years
- 210-212-8
- No Smell
- Medicine Grade
- Bromhexine
- Bromhexine hydrochloride is primarily used as a mucolytic agent to treat respiratory conditions associated with excessive or thick mucus.
- 1 to 5 micrometers
- The appearance of Bromhexine hydrochloride can vary depending on the form and brand, but here are the typical characteristics for different formulations: 1. Tablets: Shape: Usually round or oval. Color: They can be white or off-white, depending on the manufacturer. Coating: Some tablets may have a smooth or film-coated surface to make swallowing easier. 2. Syrup: Color: Typically colorless or pale yellow. Consistency: Syrup has a viscous, thick consistency, which is typical for liquid medications. 3. Inhalation Solution: Color: Clear to light yellow or colorless. Consistency: It is a thin, liquid solution intended for nebulizer or inhaler use. 4. Injectable Form: Appearance: Clear, colorless solution in vials or ampoules. The exact color and form can vary depending on the specific brand or country of manufacture, but these are the general appearances. The medication should always be checked for any signs of contamination, such as discoloration or particles, before use.
- 3.0 5.0, with an optimal pH of 4.0 .
- Powder
- 29215990
- 378.14 GSM (gm/2)
- Bromhexine hydrochloride is freely soluble in water and also soluble in alcohol. It dissolves easily, making it effective when administered in liquid forms such as syrups or solutions.
- 611-75-6
- 441.5 AdegC at 760 mmHg
- Bitter
- ~ 165-167 C (329-333 F)
- not more than 1% by weigh
- (2-amino-3,5-dibromo-1-cyclohexylmethyl)-N-cyclohexylmethylamine hydrochloride
- C14H20Br2N2 HCl
- 99
- Br | H2N-C6H12-CH2-C6H12-CH2-NH2 | Br
- Room Temperature
- not exceed 20 ppm
- Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Bromhexine HCL Trade Information
- INDIA
- Cash Against Delivery (CAD), Cash Advance (CA), Days after Acceptance (DA), Letter of Credit at Sight (Sight L/C), Letter of Credit (L/C)
- 100 Number Per Day
- 7 Days
- No
- Free samples are available
- DRUM OR BAG PACKING
- Western Europe, Middle East, Africa, South America, Eastern Europe, Asia, Australia, Central America, North America
- WE PROVIDES ALL KIND OF CERTIFICATIONS AS YOU REQUIRED
Product Description
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email








 : nilesh.sheth70
: nilesh.sheth70
